The Potable Water Treatment Ideas
Table of ContentsThe Ultimate Guide To Potable Water TreatmentNot known Incorrect Statements About Potable Water Treatment The 5-Minute Rule for Potable Water Treatment
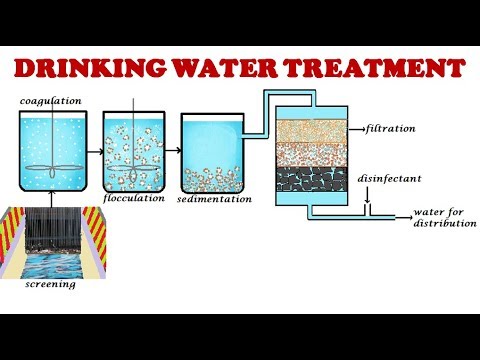
Significantly, microbial problems are commanding the attention of water treatment operators, regulators, and the media. There are numerous treatment choices to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms from drinking water. Discovering the right option for a particular supply requires sifting through a variety of often competing processes. Processes for elimination of microbes from water include pretreatment, coagulation/ flocculation/sedimentation, and purification.Filtration can be accomplished using granular media filters, slow sand, precoat filters, membranes, or other filters. Oxidants may be included to water for a variety of purposes, including control of taste and smell compounds, elimination of iron and manganese, Zebra Mussel control, and particle elimination, amongst others. For control of microorganisms within the circulation system, disinfectants should interact with germs growing in pipeline biofilms.
The Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality Final Job Force meeting (Geneva, 2003) kept in mind that finalization and progressive upgrading of the supporting file Water Treatment and Pathogen Control: Process Effectiveness in Getting Safe Drinking-water would supply substantiation and assistance to other supporting documents dealing with the problem of system safety assessment. potable water treatment. The document, which has remained in preparation for numerous years, includes a selective and succinct review of the literature, focusing on premium documents.
The Potable Water Treatment Ideas
Water treatment, likewise called sewage or domestic wastewater treatment, is a procedure by which pollutants are gotten rid of from home sewage and effluents (waste discharged from commercial plants, houses, factories) (potable water treatment). There are various processes utilized to remove these contaminants, consisting of chemical and biological processes along with physical ones. The resulting dealt with effluent must be clean enough to be released back into the environment or reused and the remaining solid waste gotten rid of off.
When it goes to a municipality's station, it undergoes numerous phases of treatment including: pre treatment, main, secondary and tertiary. Throughout pre-treatment, easily removable products are separated or screened out, including grit (sand and gravel), oils, fats and greases, and larger things (such as tampons or scraps of material). During the primary treatment, the effluent is transferred through primary clarifiers, which are large tanks where sludge settles to the bottom and greases and oils rise to the top (where they are address skimmed off).
There they can be collected and moved, and dealt with individually. Throughout the secondary treatment, aerobic biological procedures (protozoa and bacteria that consume the biodegradable soluble natural contaminants) are used to break down the biological material of the effluent (human or food waste and soaps, amongst other things). During the tertiary treatment, the quality of the effluent is raised through disinfection practices such as chlorination or making use of ozone or ultraviolet light, in addition to some other techniques such as sand purification or putting effluent in highly aerobic lagoons or built wetlands. Our consumers inform us we have, "The greatest tasting water in the world." The Home Environment Center uses a 10-stage, modern, drinking water purification system to process the water utilizing reverse osmosis water purification, ultraviolet light, and ozone to supply the best, purest, best-tasting water possible. Pollutants such as lead, nitrates, chlorine, and VOCs are eliminated.
Some Known Questions About Potable Water Treatment.
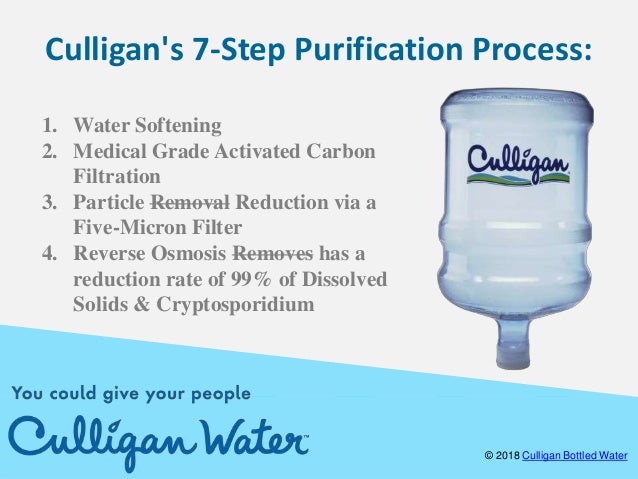
Ion exchange efficiently gets rid of the minerals accountable for "tough water" pipe scaling and deposits. The procedure also removes different heavy metals such as lead, iron, mercury, and cadmium, much of which have actually been connected with a number of well-publicized health issues. Once the water passes through the ion exchange system, it moves into the carbon purification process which gets rid of chlorine, pesticides, herbicides, and other organic pollutants including trihalomethanes (THM) s.
It's needed to remove these big particles very early while doing so to prevent fouling and obstructing of the more sensitive devices utilized at the later stages. Reverse Osmosis webpage (RO) is the focal point of the House Environment Center's water purification procedure. In our advanced reverse osmosis system, height pressure forces water throughout a membrane, leaving impurities behind.
Even the liquified impurities which can not be gotten rid of by conventional purification are captured and gotten rid of. This produces great-tasting water with a look here pureness level that goes beyond spring water, mineral, or house filtered water. This filter is designed to catch particles larger than five millionths of a meter. The filter (made up of an extruded block of carbon) provides an additional step of adsorptive capability for getting rid of chlorine and organic contaminants.
Throughout this action, the water goes through a chamber which houses a larger ultraviolet (UV) light. The UV light acts as a powerful sterilization representative. If any germs, infections, or other microbiological impurities are present, the UV light damages them. This is the first phase of chemical-free disinfection. This filter is a protective device developed to maintain system integrity during servicing so that the end product holding tank is not jeopardized.